Functions in Javascript

-A function is a reusable block of code that groups together a sequence of statements to perform a specific task.
-Function names can contain letters, digits, underscores, and dollar signs.
-JavaScript doesn't have a function data type but when we find the data type of a function using the type of operator, we find that it returns a function. This is because a function is an object in JavaScript. Ideally the data type of a function should return an object but instead, it returns a function.
SYNTAX:
function functionName(parameters) {
//function body
}
EXAMPLE:
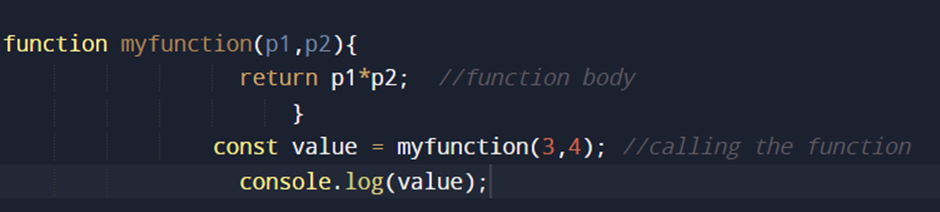
OUTPUT:

In above, P1 and P2 are the parameters.
The code inside the {} is the function body and myFunction() is the function name.
When JavaScript reaches a return statement, the function will stop executing.
Functions can be defined using:
FUNCTION DECLARATION:
Function declarations are built from:
The function keyword.
The function name.
An optional list of parameters separated by commas enclosed by a set of parentheses ().
A function body enclosed in a set of curly braces {}.
EXAMPLE:
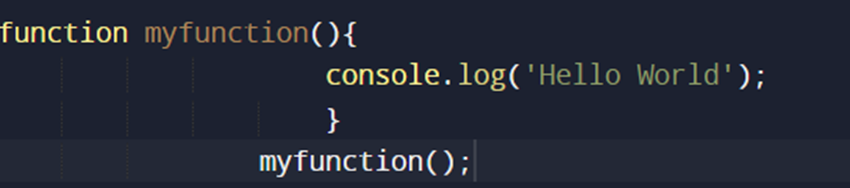
OUTPUT:
FUNCTION EXPRESSION:
Function expressions create functions inside an expression.
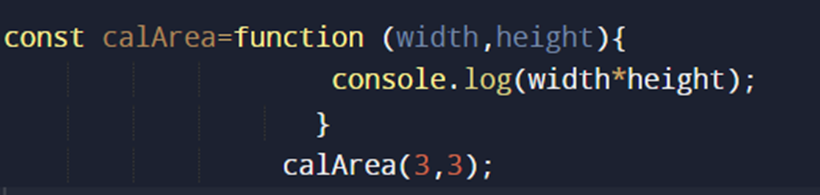
OUTPUT:

ARROW FUNCTION NOTATION:
It does not require 'function' keyword and uses a fat arrow '=>' separate the parameters from body.
Arrow functions with single parameter do not require () around parameters.
Arrow functions are always anonymous.
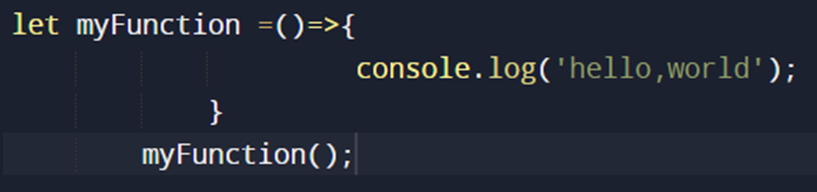
OUTPUT:
CONCISE ARROW NOTATION:
1.SINGLE-LINE BLOCK:
A single-line block function is a function that is written in a single line.
It returns the result of the expression following the arrow (=>).
It does not require the return keyword or curly braces {}.
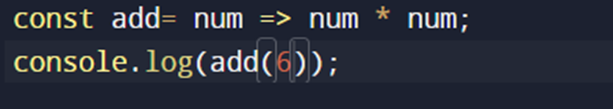
OUTPUT:

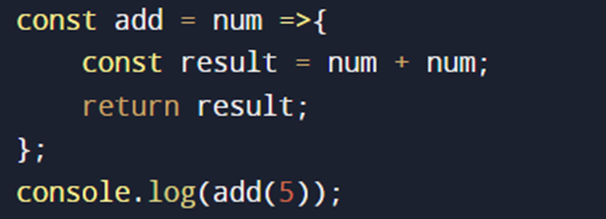
2.MULTI-LINE BLOCK:
It can contain multiple statements within its body.
The body of the function is enclosed in curly braces {} and it requires an explicit return statement to return a value.
OUTPUT:

ANONYMOUS FUNCTION:
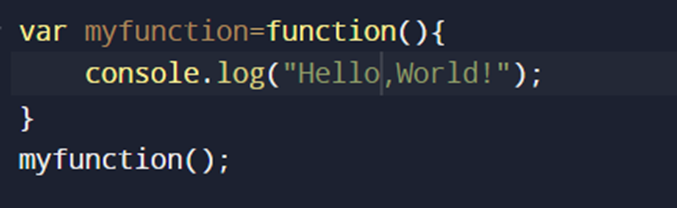
An anonymous function is a function without a name.
It can be defined using the function keyword followed by a set of parentheses () and curly braces {}, which contain the function’s code.
Anonymous functions are often stored in variable or used as callbacks.
In anonymous function, we only use function keyword without function name.
EXAMPLE:
OUTPUT:
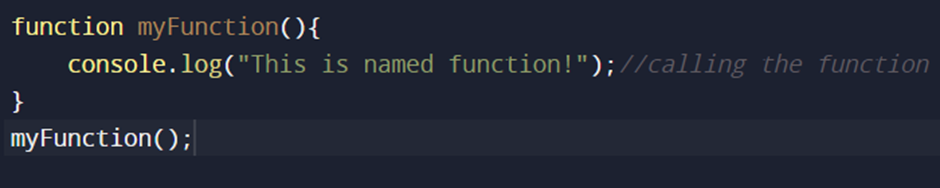
NAMED FUNCTION:
Functions with name or identifier are known as named functions.
Named functions are declared using the function keyword followed by name.
The function’s name is stored within its body.
EXAMPLE:
-Function without parameters:
OUTPUT:
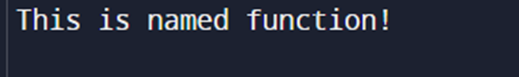
-Function with parameters:
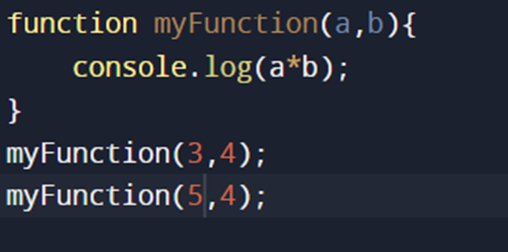
OUTPUT:

NESTED FUNCTION:
Nested function is Declaring function inside another function.
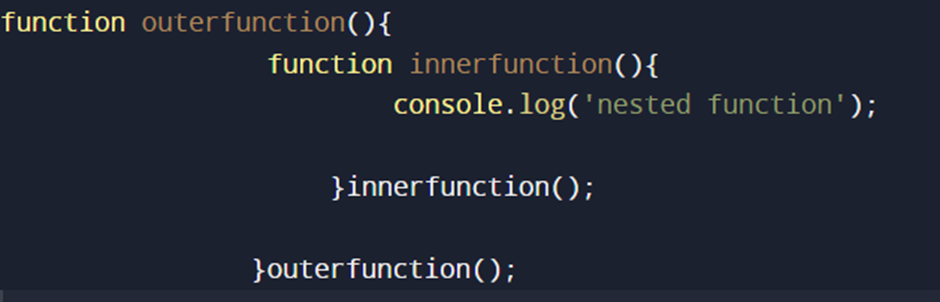
OUTPUT: