Asynchronous Programs:

What is asynchronous Programming?
- Asynchronous programming is a method of parallel computer programming that enables a process to run separately from the primary function of the program.
- Once the process completes, it communicates this information and may impact the primary function.
- Asynchronous programming often helps reduce or prevent wait times or lags in computer programming by enabling processes to continue to run in the background of the primary application.
- For example, it may prevent a cursor from taking the time to load, allowing a user to complete actions within the application more quickly.
How does asynchronous programming work?
- When you use asynchronous programming, you create an event loop. This is a process that waits for and dispatches events or messages, called a promise, in a program.
- As part of the event loop, you may create a callback, which allows the event loop to supply information from the program to another piece of code, typically the primary function of the program.
- During that time, the application can perform other tasks while you await the program. This allows potentially taxing tasks to run without forcing the user to wait for their completion.
- Await is a function or operation of many programming languages that allows asynchronous programming.
Benefits of asynchronous programming:
- It provides an improved user experience.
- It helps improve an application's performance.
- It's applicable in a broad range of programming languages.
- It can improve the speed of a program.
- It creates efficient memory management.
Example of asynchronous programming:
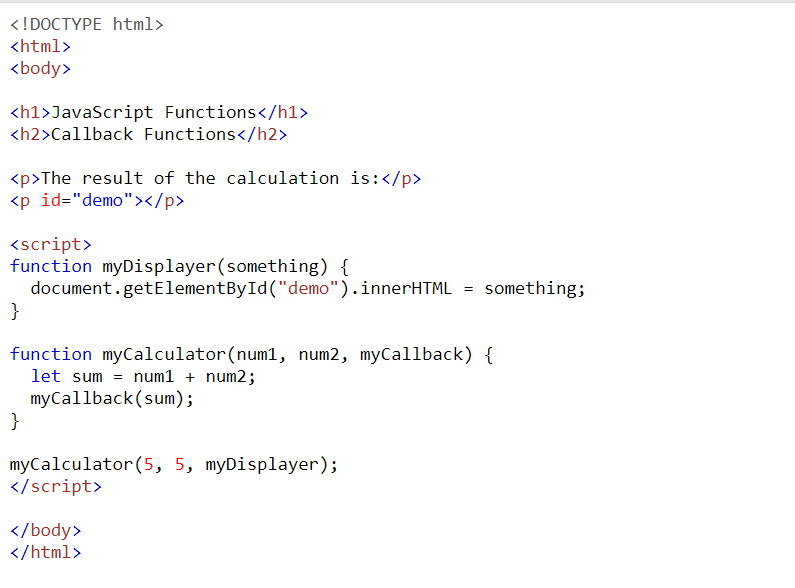
Output:




